
Main Menu

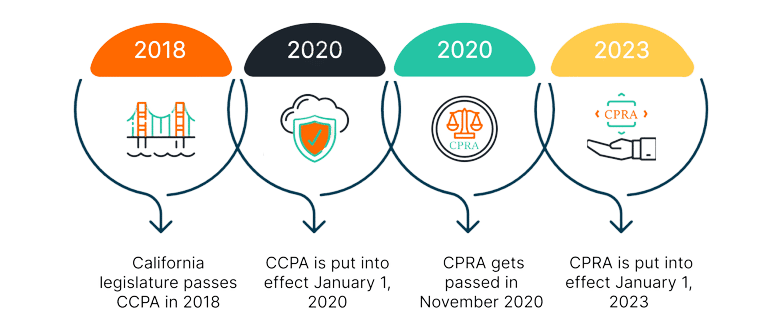
As the modern internet has changed the way we do business, The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) was created to combat growing data privacy concerns to protect human rights. The California legislature passed CCPA in 2018 and was made effective January 1, 2020. The CCPA shares a similar framework and terminology to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), establishing rights and protections for California residents and their personal identifiable information (PII). Any for-profit organization that collect consumers’ personal information, and meets one of the follow thresholds must comply:
The Right to Know
The Right to Delete
The Right to Opt-Out
The Right to Non-Discriminate
Update Privacy Policy to acknowledge that you are aware of GDPR
Review legal basis for processing personal data
Document all data is collected and processed
Data Mapping for personal information fields to each internal database
Appoint a person, team, or Data Protection Officer who can own data privacy

Reporting Metrics for auditing. Show auditors your data landscape, proof of purpose, and all data subject access requests completed to date
Meet proper deadlines (30 days to respond to requests